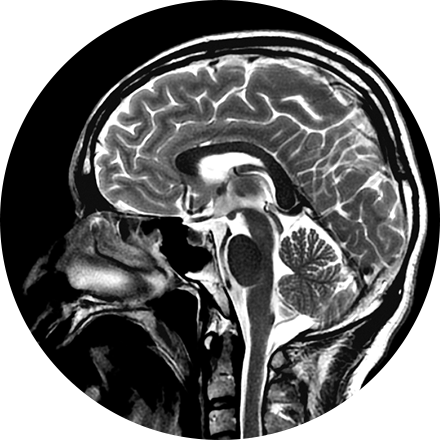
Our board-certified neuroradiologists investigate pathologies and injuries of the head, neck, and spine using the most advanced imaging technologies available. Using mainly MRI and CT, neuroradiologists diagnose abnormalities of the central and peripheral nervous system.
Some Brain & Spine Imaging Procedures Include:
X-ray is the oldest and most economical form of medical imaging. During the procedure, radiation passes through the body onto “film” (now digitized and displayed on a computer screen). In neuroimaging, spinal X-rays are used to assess for the degree of spinal motion with flexion or extension.
Neuroimaging protocols are tailored to the area of interest (brain, spine, neck, orbits, pituitary, sinuses, peripheral nerves) with both CT or MRI technique. MRI provides the highest level of anatomic soft tissue detail, so it is the optimal choice for most neuroimaging. MRI is also preferred because (unlike CT) it uses no radiation, so it is a very safe technique for the patient. CT uses radiation but is a very fast technique and has some advantages in evaluation of the bones. CT of the spine is often used to assess for successful bony fusion following spinal fusion surgery.
MR imaging of the cranial nerves uses special thin-slice sequences to screen for pathology of the cranial nerves.
Myelography is an exam in which contrast material is injected into your spinal column and then that contrast and spinal anatomy is imaged with CT technique. This allows the neuroradiologists to evaluate areas of nerve root impingement, canal narrowing, or disc protrusions. It is typically used when a patient is not a candidate for MRI.
A FDG brain PET/CT is used to image the metabolic function of the brain. Positron emission tomography (PET) uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers, a special camera, and a computer to help evaluate the brain. It is most commonly used to calculate the degree and pattern of brain volume loss, which allows the neuroradiologist to assess for different types of neurodementia syndromes. It can also help differentiate recurrent brain tumor vs. radiation change after a patient has had brain surgery. Additionally, it can help identify the seizure focus in patients with epilepsy.
Amyloid brain PET/CT is used to directly image amyloid deposition in the brain which can be found in patients with Alzheimer's Disease. This can help confirm or exclude this diagnosis in patients with memory loss. Amyloid PET can be positive in patients with Alzheimer's up to 20 years before the patient becomes symptomatic.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Applications in Advanced Neuroimaging
icobrain is a very useful quantitative volumetric AI tool that assists neuroradiologists in evaluating patients with dementia, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and brain trauma by calculating the volume of different substructures of the brain as well as brain lesions (such as white matter disease or plaques). It compares the volumes to a large normative age- and gender-matched database. This allows the neuroradiologist to know whether the degree of regional brain volume loss is more advanced than expected for the patient's age, which can aid in the diagnosis of a neurodementia syndrome (such as Alzheimer's disease) or other important medical conditions. In multiple sclerosis patients, icobrain calculates the volume and location of intracranial plaques. The software highlights new, enlarging, or shrinking plaques. It is helpful for tracking the rate of disease progression over time. icobrain has both CT and MRI applications. icobrain products in development include volumetric tumor assessment, brain myelination, assessment of brain metabolites, brain perfusion, and diffusion. icompanion is a free health app to support people with multiple sclerosis including symptom tracking, treatment reminders, and image review.
NeuroQuant (NQ) is an artificial intelligence (AI) tool that calculates the volume of different substructures of the brain and compares those to a large normative age- and gender-matched database to determine whether the degree of brain volume loss is statistically significant for patient age. This can be used to improve the early detection of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) or other neurodementia syndromes. NeuroQuant-MS is used to calculate the volume, number, and location of plaques in patients with multiple sclerosis. The software highlights new, enlarging, or shrinking plaques. This allows for accurate tracking of disease status over time. NQ can also be used to detect the location of a seizure focus in patients with epilepsy. It is also used in brain trauma patients or to assess brain development. Neuro-Quant has both MRI and CT applications. Other NeuroQuant-based AI tools in development include volumetric quantification and characterization of brain tumors.
SubtleMR is an AI tool that uses deep learning to allow an MRI of brain, spine (or any other body region) to be acquired 40-60% faster, but with higher image quality than standard scans. This is an exciting new tool that is revolutionizing MR imaging. Having faster and superior quality imaging is appealing to patients, neuroradiologists, and imaging enterprises in general.


